5 Key Steps in Effective Risk Management

Risk management is applied in most departments of an organization. Yet it’s a key part of privacy and compliance teams’ day-to-day job.
What is Risk management?
Risk management is the process of identifying and assessing risks and creating a plan to minimize or control those risks and their potential impact on an organization. A risk is a potential for loss or damage. Risks can come from a variety of places such as legal liability, natural disasters, accidents, management errors, or cybersecurity threats [1].
Let’s break the process down into the following steps:
What will the process look like?
1. Risk identification
So where do you start? One of the greatest challenges is in the very first step: identification of the risks. This step consists of three sub-steps:
Identifying your assets
In order to determine your risk exposure, you first need to centralize your assets in a register. This can be a great challenge: as you can’t protect everything, you need to identify the assets that must be protected and their priorities. An asset may be tangible (e.g., a physical item such as hardware, computing platform, network device, or another technology component) or intangible (e.g., humans, data, information, software, capability, function, service, trademark, copyright, patent, intellectual property, image, or reputation).
Identifying your threats
What’s next? After centralizing your assets, the next step is to perform a threat analysis. This threat analysis involves the identification of potential sources of harm to your identified assets. Common threats range from insider
Identifying your vulnerabilities
The final step in risk identification is to identify weaknesses in your overall security environment. These risks can make you really vulnerable to threats, for example, poor patch management.
2. Risk Analysis
The second step of risk management includes analyzing risks. The purpose of risk analysis is to assign levels to risks. A risk level can be calculated as follows:
Risk level = impact x probability
Let’s break things down again:
What is probability?
The chance of something happening (typically a threat exploiting a weakness), while the consequence is the outcome of such exploitation.
What is impact?
The severity of the risk to the rights and freedoms of the data subject.
So, how can you determine the risk level?
A risk assessment matrix is advised. This matrix will help you to determine the risk level for each identified risk, its impact and probability levels will be combined according to the risk matrix and the risk level will be determined.
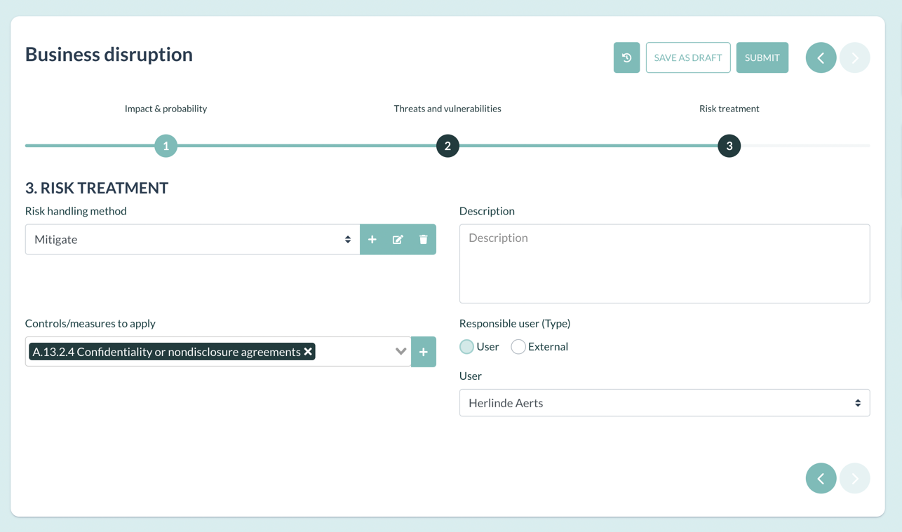
3. Risk treatment
In this step, a treatment gets implemented leading to residual risk. According to ISO 27005, which is a standard for information security risk management, available options to treat risks are:
- Risk acceptance (retention)
- Risk mitigation (modification)
- Risk transfer (sharing)
- Risk avoidance
When we look at the protection of personal data, you might be left with fewer options to work with, as the impact can be much more severe for the rights and freedoms of individuals.
When mitigation is needed, technical and organizational measures need to be implemented.
4. Risk communication
Decision-makers and other stakeholders (e.g.: customers, employees, investors,…) will have to communicate throughout the risk management process. Such information may include the existence, impact, probability, treatment, and acceptability of risks. This can be a challenge, as in many instances, stakeholders comprise a large population. Effective communication will ensure that those responsible for implementing risk management, and those with a stake in the project, where risks may occur, determine the basis on which decisions are made and why particular actions are required.
5. Risk monitoring and review
Decision-makers and other stakeholders (e.g.: customers, employees, investors,…) will have to communicate throughout the risk management process. Such information may include the existence, impact, probability, treatment, and acceptability of risks. This can be a challenge, as in many instances, stakeholders comprise a large population. Effective communication will ensure that those responsible for implementing risk management, and those with a stake in the project, where risks may occur, determine the basis on which decisions are made and why particular actions are required.
The GDPR also requires monitoring and review of risks, for example, Article 32(1) of the GDPR states:
“The controller and the processor shall implement […] a process for regularly testing, assessing and evaluating the effectiveness of technical and organizational measures for ensuring the security of the processing.”
Final thoughts
Risk management can be daunting, as all steps described above have their unique challenges. Start by defining your organization’s risk strategy and methodology. Tooling can help you to structure your approach with some also offering streamlined and automated collaboration with stakeholders. RESPONSUM has everything you need to handle your risk management challenges. Our integrated Risk Management Module facilitates collaboration and risk visibility to increase the effectiveness of your risk management programs.
Ready to try it yourself?
Book a free demo with one of our experts today! Don’t worry, they won’t bite.
[1] What is risk management? (n.d.). Red Hat – We make open source technologies for the enterprise. https://www.redhat.com/en/topics/management/what-is-risk-management
Liked reading this article? Spread the word!
Get the inside scoop on simplified privacy management
Get exclusive tips ‘n tricks straight to your inbox. Join +1,100 privacy professionals already subscribed and stay ahead of the game!

Written by
Herlinde Aerts
Product Manager @ RESPONSUM


