The Ultimate Guide to Data Protection Impact Assessments

In today’s data-driven world, organizations collect and process vast amounts of personal data, making data protection a critical concern.
Lucky for us, the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) has introduced the concept of Data Protection Impact Assessment (DPIA) as a tool to help organizations assess and manage privacy risks associated with their data processing activities.
DPIAs are like armor for organizations, protecting them from the risks of noncompliance with data protection regulations and safeguarding the rights and freedoms of individuals. In this ultimate guide, we’ll give you the lowdown on DPIAs, including what they are, when you need them, and how to conduct them like a pro.
Whether you are a data protection professional or an organization looking to protect personal data, we’ve got everything you need to know about DPIAs right here. Get ready to level up your data protection game!
What is a DPIA?
A DPIA, or Data Protection Impact Assessment, is a process that helps organizations identify and mitigate risks to the privacy rights and freedoms of individuals when processing their personal data.
What is the purpose of a DPIA?
The purpose of a DPIA is to assess the potential impact of a proposed or existing data processing activity on individuals’ privacy rights and freedoms, and to identify any measures that can be taken to reduce or eliminate these risks.
By conducting a DPIA, organizations can identify and mitigate risks before processing activities are implemented, which can help avoid potential data breaches and reputational harm.
What are specific requirements for conducting a DPIA?
The GDPR sets out specific requirements for conducting a DPIA, including the following:
- Conducting a systematic and comprehensive assessment of the risks to individuals' rights and freedoms;
- Considering the necessity and proportionality of the processing activity;
- Consulting with individuals or their representatives;
- Seeking the advice of the data protection officer (if applicable); and
- Documenting the DPIA process and outcomes
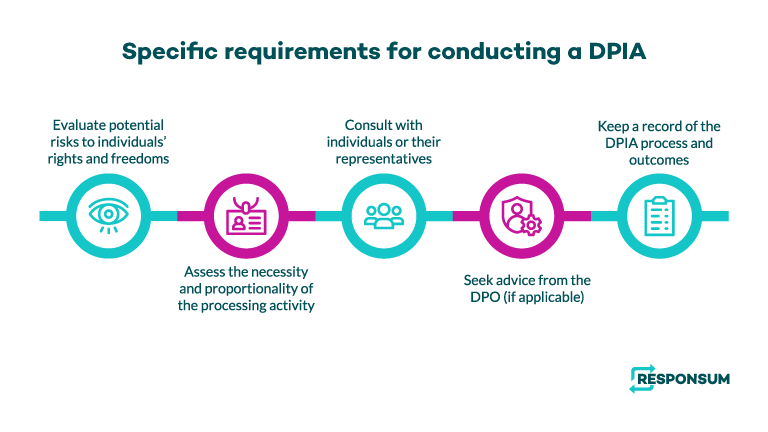
Overall, DPIAs are an important tool for organizations to ensure that they are complying with data protection regulations and protecting individuals’ privacy rights and freedoms.
When is a DPIA required under GDPR?
Under the GDPR, DPIAs are required when processing activities are likely to result in a high risk to the rights and freedoms of individuals.
The GDPR sets out the following circumstances in which a DPIA is required:
1. Processing of sensitive personal data
A DPIA is required when processing sensitive personal data, such as health data, genetic data, biometric data, or data relating to criminal convictions and offenses.
2. Large scale processing
A DPIA is required when processing personal data on a large scale. This could include processing activities that involve a large number of individuals’ personal data, or processing activities that cover a large geographical area.
3. Systematic monitoring
A DPIA is required when processing personal data through systematic monitoring of a publicly accessible area on a large scale, such as through the use of CCTV (closed-circuit television) or other surveillance systems.
4. Profiling
A DPIA is required when processing personal data through profiling, which involves the automated processing of personal data to evaluate certain personal aspects of an individual, such as their performance at work, their economic situation, their health, or their personal preferences.
5. Processing that poses a high risk to individuals' rights and freedoms
A DPIA is required when processing personal data is likely to result in a high risk to the rights and freedoms of individuals, such as where the processing involves automated decision-making with legal or similarly significant effects, or where it involves the processing of personal data on a large scale, including data concerning vulnerable individuals, children or other sensitive data.
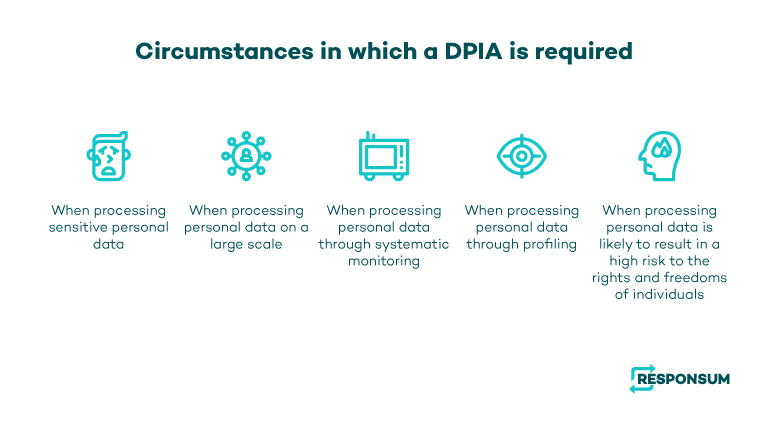
Overall, the circumstances in which a DPIA is required will depend on the specific data protection legislation in question and the nature of the processing activities involved.
Organizations should carefully assess their processing activities to determine whether a DPIA is required, and seek advice from their DPO (data protection officer) or other experts if they are uncertain.
Who should conduct a DPIA?
According to the GDPR, a DPIA must be carried out by the controller of the personal data.
The data controller is the natural or legal person, public authority, agency, or other body that determines the purposes and means of the processing of personal data.
Therefore, it is the organization or entity that collects and processes the personal data that is responsible for conducting a DPIA.
In some cases, the controller may delegate the responsibility of conducting a DPIA to a processor or a third-party consultant. However, it’s important to note that the controller remains ultimately responsible for ensuring that a DPIA is conducted when required and that the assessment is carried out effectively.
Check out our webinar: DPIA: Teamwork makes the dream work

What is the DPO's role in conducting a DPIA?
While the DPO is not necessarily the person who conducts the DPIA, they are ultimately responsible for ensuring that the DPIA is conducted correctly and in accordance with the requirements of the GDPR.
As a result, they are well-placed to perform the Pre-DPIA, as they have a good understanding of the processing activities and the potential privacy risks and impacts. However, it is important to note that the Pre-DPIA process is not mandatory under the GDPR. Instead, it is a good practice that can help organizations to assess whether a full DPIA is necessary, and to identify and address potential privacy risks and impacts at an early stage.
The DPO’s role in the DPIA process may include the following:
1. Advising on the need for a DPIA
The DPO can help the data controller determine whether a DPIA is required for a particular processing activity, based on an assessment of the risks to individuals’ rights and freedoms. To determine whether a full DPIA is necessary, the DPO may conduct a Pre-DPIA
What is a Pre-DPIA?
A Pre-DPIA (aka preliminary screening) is a process that may come before a full DPIA. The purpose of a Pre-DPIA is to assess whether a full DPIA is necessary for a particular processing activity, based on an initial analysis of the potential privacy risks and impacts.
A Pre-DPIA may be conducted when:
- There is a change to an existing processing activity, or when the new processing activity is introduced, to determine whether a full DPIA is necessary
- A processing activity involves new or emerging technologies, such as artificial intelligence or blockchain, to assess the potential privacy risks and impacts
- A processing activity involves sensitive personal data, such as health data or biometric data, to assess the potential privacy risks and impacts
The Pre-DPIA process typically involves a preliminary analysis of the processing activity, including an assessment of the data protection risks and impacts, and an evaluation of whether a full DPIA is required.
If it is determined that a full DPIA is required, the Pre-DPIA report can be used as a starting point for the full DPIA process.
2. Providing guidance on conducting a DPIA
The DPO can provide guidance on the methodology and approach for conducting a DPIA, including the assessment criteria, the risk assessment process, and the documentation requirements.
3. Ensuring the DPIA is completed
The DPO should ensure that the DPIA is completed in a timely and effective manner, and that all relevant stakeholders are involved in the process.
4. Reviewing and approving the DPIA
The DPO should review and approve the DPIA report before it is submitted to the relevant supervisory authority, to ensure that it is accurate, complete, and compliant with GDPR requirements.
5. Monitoring the implementation of the DPIA
The DPO should monitor the implementation of the DPIA’s recommendations and ensure that the privacy risks identified are adequately addressed.
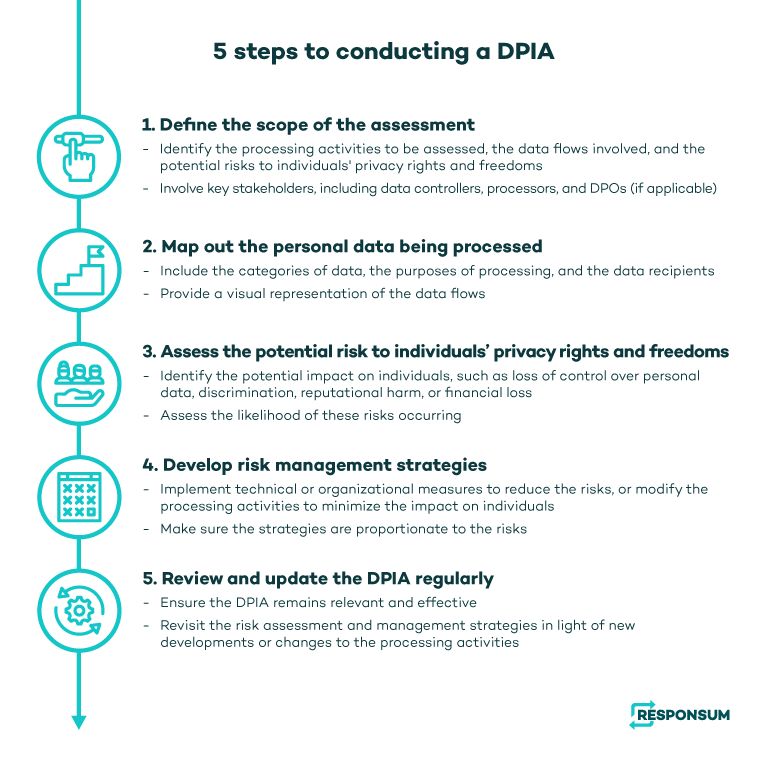
What are the steps involved in conducting a DPIA?
The process of conducting a DPIA typically involves several key steps, including scoping, data mapping, risk assessment, and risk management. Here is an overview of each step:
1. Scoping
The first step in conducting a DPIA is to define the scope of the assessment. This involves identifying the processing activities to be assessed, the data flows involved, and the potential risks to individuals’ privacy rights and freedoms. It’s important to involve key stakeholders in this process, including data controllers, processors, and data protection officers (if applicable).
2. Data mapping
The next step is to map out the personal data being processed, including the categories of data, the purposes of processing, and the data recipients. This can be done using data flow diagrams or similar tools to provide a visual representation of the data flows.
3. Risk assessment
The next step is to assess the potential risks to individuals’ privacy rights and freedoms arising from the processing activities. This involves identifying the potential impact on individuals, such as loss of control over personal data, discrimination, reputational harm, or financial loss. The likelihood of these risks occurring should also be assessed.
4. Risk management
Once the risks have been identified, the next step is to develop risk management strategies to address them. This may involve implementing technical or organizational measures to reduce the risks, or modifying the processing activities to minimize the impact on individuals. Risk management strategies should be proportionate to the risks identified and should take into account the rights and freedoms of individuals.
5. Review and update
Finally, it’s important to review and update the DPIA on a regular basis to ensure that it remains relevant and effective. This may involve revisiting the risk assessment and management strategies in light of new developments or changes to the processing activities.
Overall, conducting a DPIA requires a systematic and thorough approach, involving a range of stakeholders and a comprehensive assessment of the potential risks to individuals’ privacy rights and freedoms.
By following these steps, organizations can ensure that they comply with data protection regulations and protect the privacy of the individuals whose personal data they process.
Download our eBook for practical tips to execute quality DPIAs like a pro
Gain the confidence you need to protect personal data and comply with privacy regulations. Don’t miss out, get your copy today!
What are some key considerations to keep in mind when conducting a DPIA?
When conducting a DPIA, there are several key considerations that organizations should keep in mind to ensure that the assessment is effective and meets the requirements of data protection regulations. Here are some important considerations:
1. Involving data subjects
It’s important to involve data subjects in the DPIA process to ensure that their rights and interests are taken into account. This may involve consulting with data subjects or their representatives, such as through focus groups, surveys, or other means. By involving data subjects in the DPIA process, organizations can gain a better understanding of the potential impact of the processing activities on individuals and tailor risk management strategies accordingly.
2. Documenting the DPIA process
It’s important to document the DPIA process in detail, including the scope of the assessment, the data mapping exercise, the risk assessment and management strategies, and any other relevant information. This documentation should be kept up to date and made available to relevant stakeholders, such as data protection authorities, if requested.
3. Consulting with data protection authorities
Depending on the nature of the processing activities, it may be necessary to consult with data protection authorities during the DPIA process. This may involve seeking guidance on specific aspects of the assessment or obtaining approval for the processing activities. Organizations should familiarize themselves with the relevant data protection regulations to determine when consultation with data protection authorities is required.
Which are relevant data protection authorities?
When it comes to DPIAs, the relevant data protection authorities are both the national Data Protection Authorities (DPAs) in each EU member state and the European Data Protection Board (EDPB). These entities are responsible for enforcing data protection regulations and ensuring that organizations comply with the GDPR and other applicable data protection laws within their jurisdictions.
Each member state has its DPA, which is accountable for supervising the processing of personal data within its jurisdiction. DPAs have broad authority, including the ability to conduct inspections and investigations, issue fines, and require organizations to take corrective action if they are found to be in violation of data protection regulations.
The EDPB, on the other hand, is an independent European body that works to ensure the uniform application of data protection rules across the EU. It provides guidance on conducting DPIAs and enforcing data protection regulations, and it has the power to make binding decisions in certain cases and coordinate the activities of national DPAs.
4. Integrating DPIA into organizational processes
Conducting a DPIA should not be a one-off exercise, but rather an ongoing process that is integrated into organizational processes. This may involve incorporating DPIA into project management processes or risk management frameworks to ensure that privacy considerations are taken into account throughout the lifecycle of processing activities.
5. Ensuring transparency
Finally, it’s important to ensure transparency throughout the DPIA process, both with respect to data subjects and other relevant stakeholders. This may involve providing clear and concise information about the processing activities and their potential impact on individuals, as well as making the DPIA documentation available to relevant stakeholders upon request.
Overall, conducting a DPIA requires a careful and systematic approach that takes into account the interests and rights of data subjects, involves consultation with relevant stakeholders, and is documented and integrated into organizational processes. By following these considerations, organizations can ensure that they comply with data protection regulations and effectively manage the risks associated with processing personal data.
DPIA tools and resources
There are several great tools and resources available to organizations that are looking to conduct a DPIA. By leveraging these resources, organizations can ensure that their DPIA process is thorough, effective, and compliant with data protection regulations. Here are some examples:
DPIA templates
Many data protection authorities, such as the ICO in the UK and the CNIL in France, provide DPIA templates that can help organizations structure and document their DPIA process.
Guidelines and checklists
Several organizations, such as the International Association of Privacy Professionals (IAPP), provide guidelines and checklists that can help organizations conduct a DPIA. These resources often include step-by-step instructions, best practices, and risk assessment frameworks.
DPIA software
There are several DPIA software tools available that can help automate the DPIA process, including data mapping, risk assessment, and documentation. These tools often include pre-built templates, workflows, and reporting features.
Industry-specific guidance
Some industries, such as healthcare and finance, have specific regulations and guidelines that require organizations to conduct DPIAs. There are several industry-specific resources available that provide guidance on conducting DPIAs in these contexts.
Expert consultants
Finally, organizations can engage expert consultants who specialize in data protection and privacy to assist with conducting a DPIA. These consultants can provide valuable guidance on best practices, regulatory requirements, and risk management strategies.

What are the best practices for conducting a DPIA?
Here are some DPIA best practices to consider when conducting a Data Protection Impact Assessment:
1. Maintain transparency
It’s important to be transparent with data subjects about the processing activities being conducted and how their personal data is being used. This can help build trust and ensure that data subjects are fully informed about their rights and how to exercise them.
2. Involve key stakeholders
DPIAs should involve all relevant stakeholders, including IT, legal, compliance, and security teams. This ensures that all risks and issues are identified and addressed, and that the DPIA is comprehensive and effective.
Don’t forget to involve data subjects wherever possible, particularly if the processing activities are likely to have a significant impact on their privacy rights. This includes providing information about the DPIA process and seeking input on the processing activities and any concerns they may have.
3. Consider the full data lifecycle
DPIAs should consider the entire data lifecycle, from collection to deletion, and identify potential risks and issues at each stage. This includes understanding the purposes for which data is collected, how it is processed, who has access to it, and how it is stored and protected.

4. Adopt a risk-based approach
DPIAs should adopt a risk-based approach, assessing the potential impact of data processing activities on data subjects and identifying and mitigating risks. This includes assessing the likelihood and severity of harm, and considering the effectiveness of controls and safeguards.
5. Document the DPIA process
It’s important to document the DPIA process, including the methodology used, the risks and issues identified, and the actions taken to mitigate those risks. This documentation can be used to demonstrate compliance with data protection regulations and to identify areas for improvement.
Liked reading this article? Spread the word!
Get the inside scoop on simplified privacy management
Get exclusive tips ‘n tricks straight to your inbox. Join +1,100 privacy professionals already subscribed and stay ahead of the game!

Written by
Yannick Vranckx
Marketing Specialist @ RESPONSUM